The word “landmark” is an Olde English word originally used to describe the expansion of the boundaries of a kingdom. Nowadays, this word is typically reserved to describe changes in legislation which will have a massive impact on our lives. I think it’s fair to use this word to describe two speech acquisition data studies that came out right before the pandemic and that have huge implications for how we do our jobs as SLPs.
New speech acquisition data published by Dr. Sharynne McLeod and Dr. Kate Crowe challenges some long-held beliefs about how and when sounds emerge. Results suggests that developmental norms are common across all languages, initial sounds develop as early as age 2, and the majority of sounds are mastered by age 5, including the American /r/.
We sat down with Dr. Sharynne McLeod of Charles Sturt University in Bathurst, Australia and had a lively conversation about the results of the cumulative research she has led and been part of. Here is a quick recap and four take-aways from the conversation.
Dr. McLeod spoke at the Bilinguistics 2023 SLP Conference on Speech Sound Disorders. People raved about her presentation. It was incredible. You can still catch the talk inside of SLP Impact.
Important Take-Aways from These Decades of Research on Speech Acquisition Data
Dr. Sharynne McLeod is so easy to listen to and her humility is pervasive in everything she shares. If you are new to her work, there are some things we don’t want to skip past: Her work spans decades. She received funding and traveled extensively to the countries of many of the languages she studied. She purchased and explored oodles of evaluations tools in multiple languages to understand the normative data on which they are based. Her country is her lab: The people working with and for her are out in the rural communities, towns, and urban centers of Australia.
And what is the result? Possibly the greatest data set accumulated on speech acquisition. Here are four ideas that can have an immediate impact on your work.
1. Children Are Able to Produce Almost Every Consonant in Their Language By Age 5
Regardless of the language, most sounds are acquired by the time Kindergarten starts in the US. Think about this. Think about the amount of time it takes the average child to make it through the referral process when the teacher can’t understand them. Think about the relationship between linguistic phonology and the growth of phonology as it relates to reading.
An important distinction that she made was that occasionally there is a remnant phoneme such as /th/ that older kids still may need to focus on. However, nearly all sounds and, clearly, intelligibility is normalized by 60 months.
My take-aways: I am questioning the weightiness of the referral process in many of the schools I work in. I know that many of my students do not have any academic experience when they start Kindergarten and we need to give them a few months. But if they have been in Head Start or Pre-K or if it is spring of the Kindergarten year, we need to move the process along. I also think that I can do a great job supporting Kindergarten and Pre-K teachers in the interim.
2. Developmental Norms are Similar Across All Languages
The process of identifying which sounds to work on with a bilingual child has four parts:
- Test them in English and identify which sounds are being said in error
- Check! Not a problem.
- Find out if those sounds exist in the home language, so we can separate second-language influence from true difficulty
- Okay here! I can compare the sound systems of two languages.
- Make sure the sounds can be used in the same way/position in both languages. An easily understood example is that Spanish has B, P, M, W, G, and K. However, these don’t exist in final position. So they shouldn’t be probed as final consonants English words.
- Not as easy but I can ask a native speaker pretty quickly or look at word charts.
- Make sure that the sounds come in at the same age so we don’t misdiagnose based on age of acquisition
- This has always been the bugger! Even in our research to write Difference or Disorder we had to really dig to find speech acquisition data in the most common languages we treat. But what about Hmong, Igbo, Telugu… Good luck! Either we don’t have the data or more likely it was conducted by other professionals like child psychologists and published in the native language. This makes it difficult to find.
Here is an Arabic speech acquisition data chart that is a great example of information that is actually quite rare for English-speaking professionals.
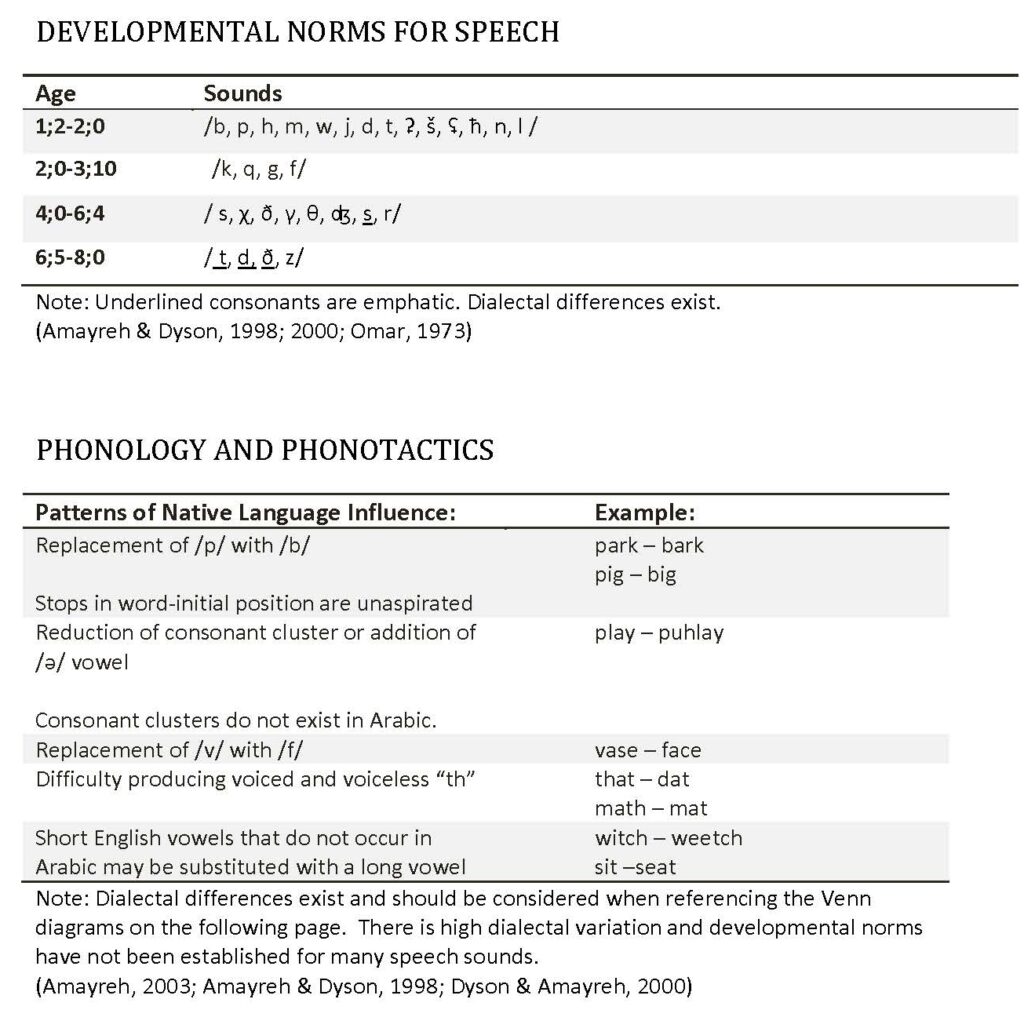
My take-aways: These new data suggests we can work with one set of norms and therefore evaluate more accurately and quickly.
3. Initial Sounds May Develop at a Younger Age Than Expected
I’m dating myself here and admitting a fondness for beautiful speech acquisition charts on Pinterest, BUT… most images and data sets available to us start at age three. This is troubling for me when viewing the tree house chart down below. Reason being, I am wondering if early intervention programs need to be revisiting their admission criteria. I question the goals I wrote early in my career during my ECI home visits.
My take-aways: When working with and diagnosing the very young children, my goals should reflect the new norms. Also, I need to expect more out of the little guys. Yes, they are typically a lot of fun, but we need to go to work! I need to be targeting /t/, /k/, /g/, /ng/, /f/, and /y/.
4. The American English R Develops Early Than What Has Been Cited in the Literature and is the Same as Other Languages
Yes, /r/ is a later sound, explains Dr. McLeod. However, the collective research suggests it develops at age 5, not 6, 7, or 8.
My take-aways: How many times have I been in conversations with first-grade teachers and said “let’s wait and see.” Hmmmm…. There is part of me that is so, so relieved by these findings. I have often felt that by working with bilingual populations I have had split personalities.
“Here is me working in Spanish and this is what I focus on.”
“Here is me working in English and this is what I focus on.”
“Here is me working in Arabic/Mandarin/… and this is what I focus on.”
But I knew in my heart that the Spanish-speaking kids were pulling off /r/ at five and six (per Spanish-norms) and even the trilled /rr/! Yes, the American English R(s) are complex. But three more years needed to master it? First graders beware. I’m coming for you.

American Speech Acquisition Data
There was a point during our conversation where Dr. McLeod shared that American developmental norms are not necessarily published in journals but are instead published in test manuals. This led to their follow-up study in 2020 where they focused exclusively on American English, redrawing the lines as to when the English /r/ is expected to come in.
Several poster downloads were created to easily display the data and are available on the Charles Sturt University Speech Acquisition page. Comparing the international data set and the English data sets, the outlying /th/ sound is the major difference between languages. It should also be noted that most US norms begin at age three and the compilation of the numerous speech acquisition data studies showed that the first sounds occur earlier.

Resources
The two primary speech acquisition data research studies of note are the 2018 and 2020 studies that Dr. McLeod carried out with Dr. Kathryn Crowe. Additionally, this research has been going on over several years and can be found in research panels and published texts.
Crowe, Kathryn, and Sharynne McLeod. “Children’s English consonant acquisition in the United States: A review.” American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology 29.4 (2020): 2155-2169.
McLeod, Sharynne, and Kathryn Crowe. “Children’s consonant acquisition in 27 languages: A cross-linguistic review.” American journal of speech-language pathology 27.4 (2018): 1546-1571.
International Expert Panel on Multilingual Children’s Speech (2012). Multilingual children with speech sound disorders: Position paper. Bathurst, Australia: Research Institute for Professional Practice, Learning and Education (RIPPLE), Charles Sturt University.
McLeod, S. (2012). Multilingual children’s speech. Bathurst, NSW, Australia: Charles Sturt University.




